- Peer-reviewed article in Vaccine addresses the 4As of vaccine access – availability, affordability, adoption and alliances
- Paper’s recommendations offer insights on how to achieve the Decade of Vaccine’s goal of 90% global vaccine coverage by 2020.
- Increased vaccine awareness, predictable demand, and sustainable financing among 26 expert recommendations to support vaccine access and innovation
A newly-published paper on vaccines provides a set of pragmatic actions to improve global access to and use of high quality, safe and effective vaccines. Published in Vaccine, the peer-reviewed paper, ‘Delivering the promise of the Decade of Vaccines: opportunities and challenges in the development of high quality new vaccines,’
was authored by vaccine experts with support from the International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Associations (IFPMA) and the Biotechnology Industry Organization (BIO).
Launched in 2010, the Decade of Vaccines (DoV) Initiative assembles key global health stakeholders in an effort to reduce vaccine-preventable illnesses by achieving 90 percent global vaccine coverage by 2020. The paper provides the perspectives of the research-based vaccine industry on how to advance the DoV’s objectives and support vaccine uptake by addressing availability, affordability, adoption and alliances.
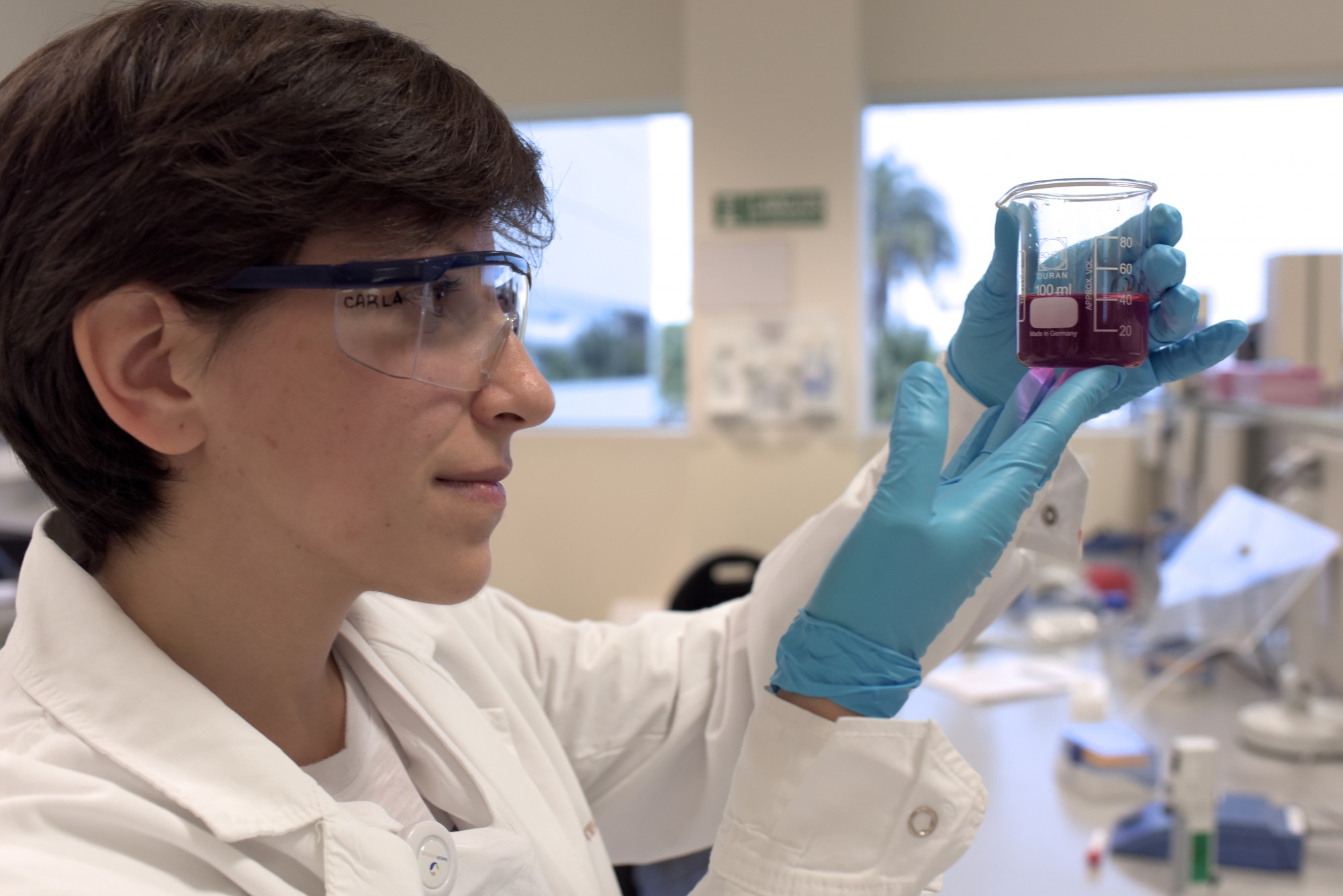
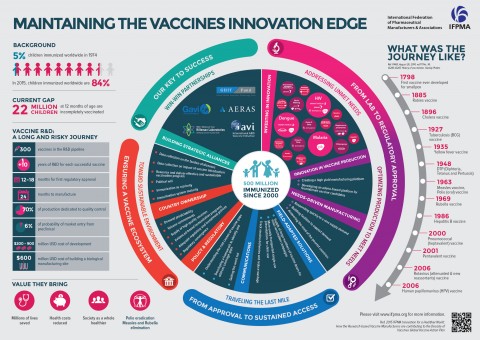
Over the last 30 years, vaccine development has accelerated due to scientific breakthroughs in biotechnology, genetic decoding and information technology. The result is a broad range of new vaccines targeting 25 infectious disease categories. Today, vaccines are helping to combat major life-threatening diseases — including cervical cancer, which affects 500,000 women each year, and pneumococcal disease, responsible for 1.6 million deaths each year.
Despite important health advances associated with vaccine innovation, barriers to equitable and sustained global access remain. As the global community strives to address those barriers, the authors warn against interventions that fail to reconcile the needs of both access and innovation.
According to the authors, accelerating vaccine access and innovation, especially in the developing world, requires a mix of “push and pull” mechanisms. Examples of “push” mechanisms that stimulate R&D are grants and investment tax credits, while “pull” mechanisms can include donor guarantees of vaccine purchases and government programs to promote vaccine uptake through increased awareness of vaccines’ health benefits.
“Global health stakeholders share responsibility for achieving the goals of the Decade of Vaccines,” says Eduardo Pisani, IFPMA Director General. “This report applies industry learnings and expertise that contributed to several past health successes such as dramatically reduced measles-related deaths and eradication of smallpox. With greater public awareness and access to innovative vaccines, great strides can be made toward preventing other leading communicable and non-communicable diseases.”
“These innovative approaches to achieving equitable and sustained global access to high quality, safe and effective vaccines can potentially save millions of lives, dramatically enhance economic productivity, and reduce under-five mortality,” said Jim Greenwood, BIO’s President and CEO.
The paper, ‘Delivering the promise of the Decade of Vaccines: opportunities and challenges in the development of high quality new vaccines,’ can be viewed at: Vaccine report. Also IFPMA and BIO developed two infographics – Vaccine R&D and Innovative Vaccines Companies and the Decade of Vaccines – as useful resources.