Inventing
Medicines and Vaccines
Economic footprint
Wirkstofflager, Roboter, Platten, Mitarbeitende
Economic footprint of our industry
Our biopharmaceutical industry makes an important and diversified contribution to the global economy. We support research on the economic contribution of our industry to have a better understanding of our impact and more accurately guide policymaking.
Our economic footprint:
- Our medicines and vaccines save lives, reduce hospitalization, and make society as a whole healthier and more productive. Yet our contribution to society goes beyond health;
- It is a sector that generates jobs, tax revenues, and contributes to technology diffusion or put simply how people adopt and benefit from the innovation we bring;
- Our big investment in R&D and innovation also helps drive technological development.



Our industry makes major contributions to the prosperity of the world economy. It is a robust sector that has been one of the pillars of industrialized economies and is also increasingly recognized as an important sector in the developing world as well. It contributes to employment (direct, indirect, and induced), trade, research and development (R&D) investments, and technological capacity building. It is also a necessary foundation for the existence of the generic industry.
The economic footprint of our industry is most visible in the form of investments in manufacturing and R&D. Globally, the production value of the biopharma industry amounted to USD 1.2 trillion in 2018, more than USD 200 billion higher than in 2014. The innovative biopharmaceutical industry is estimated to have invested USD 179 billion globally on biopharmaceutical R&D in 2018.
In 2017, the biopharmaceutical industry directly added roughly the GDP of the Netherlands (USD 532 billion) to the world economy. In addition to the immediate economic effects it directly generates, industry also supported the global GDP with an additional USD 791 billion triggered by its consumption of intermediate inputs from other sectors through its global value chains. Example of these intermediates include chemical compounds and active ingredients used in other industries. Moreover, the private consumption triggered by directly and indirectly generated income resulted in an extra USD 515 billion of GDP contribution to the global economy through induced effects. Therefore, combining direct, indirect and induced effects, the biopharmaceutical industry’s total contribution to the world’s GDP is USD 1,838 billion.
Our industry also contributes to job creation in both developing and developed countries. In 2017, it employed approximately 5.5 million people worldwide (including generics); a 1.1 million increase from 2012. In 2017, in the United States, spending on services and supplies totaled USD 589 billion, translating into more than 4 million jobs in this country.
On top of directly or indirectly creating jobs, the biopharmaceutical industry’s presence also leads to dissemination of knowledge in the workforce. Employees working for a biopharmaceutical company often receive qualified training and are exposed to new technologies and processes. This knowledge becomes an asset for the entire workforce, as the employees may later change jobs or start their own companies, hence fostering economic development.
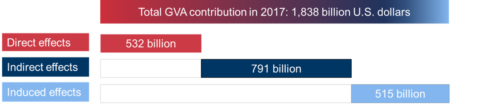
Source: WifOR (2020) The Global Economic Footprint of the Pharmaceutical Industry
There is no doubt our industry contribution to society is significant. Compared to other industries, did you know that, in 2018, the pharma industry spent every year seven times more than the defence & aerospace industries combined?
5.5 million
people employed by the pharmaceutical industry globally
USD 1.8 billion
total gross value added by the biopharmaceutical industry in 2017
USD 179 billion
global investment in biopharmaceutical R&D in 2018









