Inventing
Medicines and Vaccines
Sustainable innovation
Innovation environment
Innovation in our industry is about creating and improving medicines and vaccines for patients who need them, and allowing the greatest choice of treatments for doctors with health outcomes that matter.
- Innovation means a lot of things. It happens when we challenge the status quo and the ‘business as usual’ realities, and
- Most of the innovations brought in by our industry are borne from rigor, discipline, risks taking, time, money, and collaboration. A successful innovation process is one that minimizes the time and cost needed to translate a scientific “idea” to an approved new safe and effective medicine or vaccine that ultimately will benefit patients.


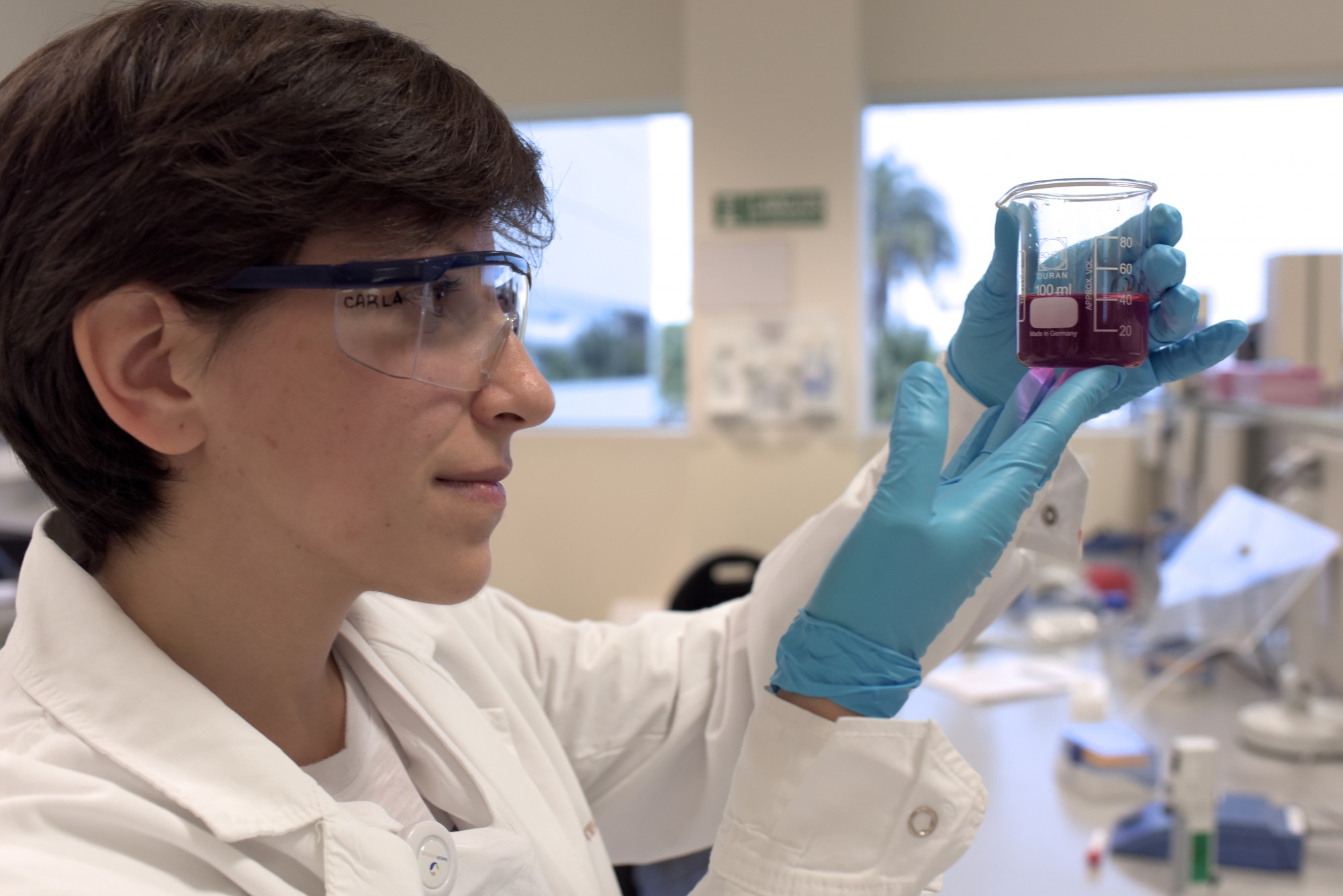
Innovation in our field is an exciting, complex, and creative process that includes far more than pharmaceutical Research & Development (R&D) alone. Imagination, ideas, possibilities, connecting the dots with a diversity of people, these altogether prompt us to discover today’s medicines.
Historically, most of pharma R&D has taken place in higher-income countries. However, in today’s globalized, interconnected, and fast-moving world, there is a growing need to empower people worldwide to find creative solutions to the different health challenges they face.
Governments have a variety of tools available to encourage a favourable environment for each stage of the R&D process, from basic research to clinical trials.
At the most basic level, policies to nurture domestic scientific communities and develop stable and transparent legal systems go a long way in encouraging innovation. Stability in industrial and healthcare policy helps reduce the investment risks of innovators in both the public and private sectors by encouraging them to develop the sort of long-term research plans and investment projects that characterize the pharmaceutical industry. Upgrading the levels of education and skills in the science stream is a necessary condition to contribute to each stage of the pharma innovation process, from the earliest days of product development to large-scale clinical testing. Countries with strong education systems contribute to a dynamic workforce that can sustainably replenish research positions over generations.
Effective intellectual property systems – including protection of patents, trademarks, and proprietary data – are critical for stimulating R&D. They provide some assurance that, if a new medicine is successfully approved, the innovator has a chance to generate revenues sufficient enough to justify the investments in R&D and so ensure sustainable innovation into the future.

Medical technologies that benefit patients and manufacturers alike are possible only with huge R&D investments and the protection of intellectual property that make those investments feasible.
340
new drugs delivered since 2002
50
new pharmaceuticals were launched in 2014, out of more than 7,000 compounds in development.
Every USD 1
spent on new medicines for congestive heart failure in the US saves USD 8.3 in medical spending