Tackling
Global health challenges
Antimicrobial resistance
Gloved hand holding a Petri dish with bacteriaю
Antimicrobial Resistance
The rapid development and spread of AMR is a global public health crisis, undermining the many advances in medical treatment that are underpinned by the availability of safe and effective antimicrobials.
We now face the possibility of a future without effective antimicrobials, where preventing and treating infectious diseases will become more challenging and where even common medical treatments and simple surgeries such as cancer chemotherapy and caesarean sections will carry significantly higher risks for patients. Simple infections could become a deadly threat not only for the most fragile, but also any healthy person.


AMR is a global problem. Resistant bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens know no borders. There are growing concerns that resistance is outpacing new therapies. Antibiotic discovery and development presents specific scientific, regulatory, and economic challenges.
Antibiotic stewardship must also be an integral part of any solution to overcome antibiotic resistance. Cases where antibiotics are overused or misused exist worldwide, so it is imperative to ensure that each patient receives the right antibiotic for the right pathogen at the right time. At the same time, somewhat perversely, overuse co-exists with lack of access to antibiotics in low- and middle-income countries.
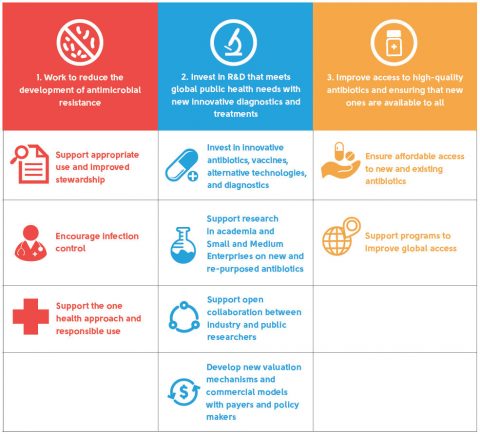
The complex social, scientific, and economic issues driving AMR cannot be resolved without strong collaboration between the private and public sectors. Protecting patients and counteracting a public health crisis, which can potentially undermine entire health systems, requires a coordinated global response by all stakeholders, including governments, civil society, academia, international health agencies, health care providers, and the life sciences industry.
Diverse stakeholders, including the United Nations, the World Health Organization, the Wellcome Trust, and leading governments, have recognized the vital role the biopharmaceutical sector is playing to reduce antimicrobial resistance and develop new antibiotics to fight infections. The AMR Industry Alliance, a group of more than 100 biotech, diagnostic, pharmaceutical, and generic drug companies, is working to address this scourge, which is now responsible for 700,000 deaths a year and could cost the global economy up to $100 trillion between now and 2050 unless urgent actions are taken.
The growth of resistance combined with the high attrition rate of antibiotic drugs in development makes it crucial that enhanced investments be made in research and development to ensure that a sufficient pool of antibiotics is available at any time to treat common and rare infections. The recent discovery of new antibiotics should not disrupt sustained efforts in discovering new antibiotics. The fight against antimicrobial resistance is a long term one as new antibiotics will always be needed.
10 million
people may die every year from bacterial infection in 2050
US$ 1.6B
Invested by biopharmaceutical companies in 2018 into the development of AMR-relevant products
100+
Life science companies are part of a ground-breaking alliance